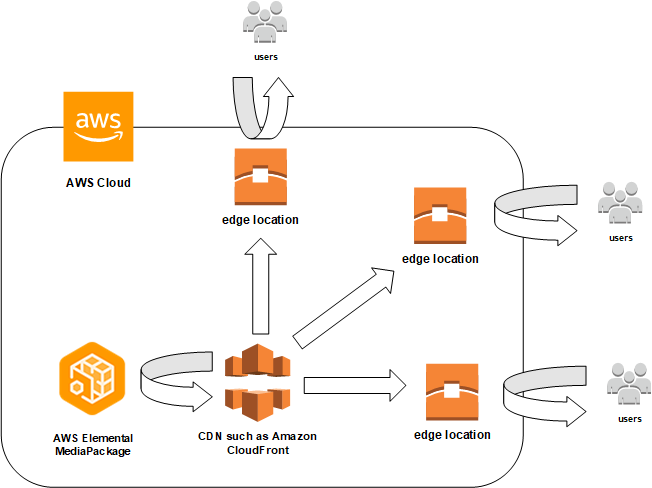
What is CloudFront?
CloudFront is a Content Delivery Network (CDN) service by AWS that delivers data (static/dynamic content, videos, APIs) to users via edge locations, reducing latency and improving website/application performance.
How CloudFront Works:
- Edge Locations: Requests are served from the nearest edge location.
- First request: If the content is not cached, CloudFront retrieves it from the origin server (e.g., EC2, S3).
- Subsequent requests: Cached data is delivered from the edge location, reducing response time.
X-Cache: Miss from CloudFront→ First request.X-Cache: Hit from CloudFront→ Cached response.
- Origins:
- CloudFront supports origins like EC2 instances, S3 buckets, or custom servers.
Practical Setup Examples:
1. CloudFront with EC2 and NGINX
- Step 1:
- Launch an EC2 instance and install NGINX to serve content.
- Access it via its Public DNS to verify.
- Step 2:
- Go to CloudFront, create a distribution.
- Use the EC2 Public DNS as the origin.
- Set cache policies (
TTL: Min, Max) to define caching behavior. - Step 3:
- Access the CloudFront distribution URL.
- Check the Network Tab in the browser:
- First load →
X-Cache: Miss from CloudFront. - Reload →
X-Cache: Hit from CloudFront.
Update CloudFront Cache:
- If you update NGINX data on EC2, use Invalidation in CloudFront to clear the cache and fetch updated content.
Restrict Direct Access to EC2:
- Modify EC2 security groups to allow access only from CloudFront’s IP range (e.g., using VPC Prefix List like
pl-9aa247f3). - Verify direct EC2 access is blocked.
2. CloudFront with S3 Bucket
- Step 1:
- Create a private S3 bucket.
- Step 2:
- Go to CloudFront, create a distribution.
- Use the bucket as the origin and enable Origin Access Control (OAC).
- Step 3:
- Update the S3 bucket policy to allow CloudFront access only.
- Step 4:
- Access content via CloudFront URL.
Example S3 URL:
https://d19rtz27njb4da.cloudfront.net/image/load.png
3. Path-Based Routing in CloudFront
Use CloudFront to route requests to multiple origins based on the path:
/s3→ S3 bucket./orindex.html→ EC2 instance.
Steps:
- Setup both EC2 and S3 as origins.
- In CloudFront, create behaviors:
- Define path patterns (e.g.,
/s3). - Set corresponding origins.
- Test by accessing CloudFront URLs.
Why CloudFront Takes Time to Deploy:
CloudFront propagates its configurations across all edge locations, which takes time.
Deleting a Distribution:
- Disable the distribution first.
- Once disabled, you can delete it.
Additional Topics to Explore:
- CloudFront with API Gateway for dynamic APIs.
- Geo-Restrictions to limit content delivery to specific regions.
- Custom SSL/TLS Certificates for HTTPS support.
- Field-Level Encryption for securing sensitive data.
- Monitoring with AWS CloudWatch for performance metrics.
Summary:
AWS CloudFront is a powerful CDN for delivering content globally with low latency. It works seamlessly with EC2, S3, and other AWS services while supporting caching, security, and path-based routing. Understanding setup, caching behaviors, and invalidations ensures optimal performance.