AWS provides robust storage solutions with features like multi-attach EBS volumes and snapshots, which allow you to store, back up, and share data effectively across instances. Here's a detailed guide and workflow for implementing multi-attach volumes, understanding IOPS and throughput, and managing snapshots.
Multi-Attach Volumes in AWS
What are Multi-Attach Volumes?
- Multi-Attach is a feature for Amazon EBS io1/io2 volumes that allows multiple EC2 instances in the same Availability Zone to access a single volume simultaneously.
- Useful for clustered applications requiring shared storage.
- Supported Instances: Not all instance types (e.g.,
t2.micro) support Multi-Attach. You need to use supported types such asm5.largeor above.
Steps to Configure Multi-Attach Volumes
- Create a Multi-Attach Enabled Volume:
- While creating an EBS volume, choose
io1orio2as the volume type. - Enable the Multi-Attach option during creation.
- Attach Volume to Multiple Instances:
- Attach the volume to multiple supported instances within the same AZ.
- When attaching, note that Linux might internally rename devices (e.g.,
/dev/sdfto/dev/xvdf).
- Verify Multi-Attach Configuration:
- Log in to both instances.
- Use the
lsblkcommand to verify the volume is attached:
lsblk
- The volume will be listed under both instances.
- File System Consideration:
- Use a cluster-aware file system (e.g., GFS2 or OCFS2) for read/write access from multiple instances.
When to Use Multi-Attach Volumes
- Shared file systems for clustered applications.
- High-availability setups where multiple nodes need access to the same data.
- Real-time data processing in distributed systems.
Understanding EBS Volume Types, IOPS, and Throughput
Volume Types:
- General Purpose SSD (gp2, gp3):
- Best for most workloads.
- Balanced cost, performance, and scalability.
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1, io2):
- High performance with customizable IOPS.
- Ideal for database workloads.
- Throughput Optimized HDD (st1):
- Optimized for high-throughput, low-cost workloads.
- Best for log processing and large file storage.
- Cold HDD (sc1):
- Lowest cost, high latency.
- Suitable for cold data archiving.
IOPS and Throughput:
- IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second):
- Determines the number of read/write operations a volume can handle per second.
- Increases with volume size for gp2 (up to 16,000) and is configurable for io1/io2.
- Throughput:
- Measures the data transfer rate (MB/s).
- Higher for throughput-optimized types (e.g., st1).
When IOPS Changes:
- Scaling up volume size or switching to
io1/io2increases IOPS. - gp3 allows independent scaling of IOPS and throughput.
Snapshots in AWS
What is a Snapshot?
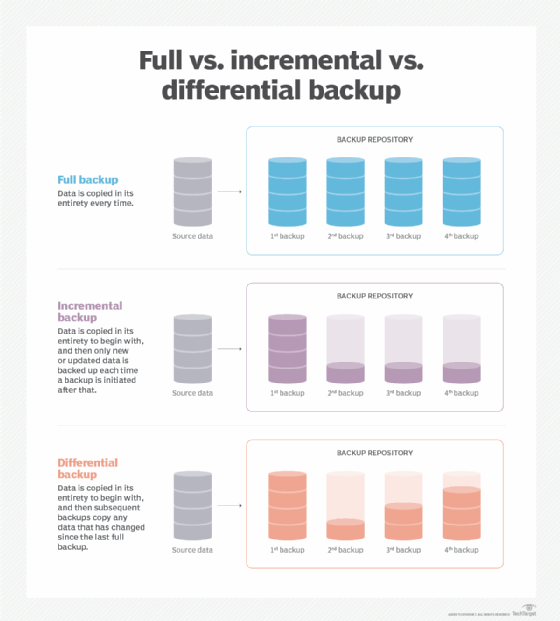
- A snapshot is a point-in-time backup of an EBS volume.
- Incremental Backup: After the first full snapshot, subsequent snapshots only store changes, reducing storage costs.
- Storage Location: Snapshots are stored in Amazon S3.
Steps to Create and Verify a Snapshot
- Create a Snapshot:
- Navigate to the AWS Management Console > EBS > Snapshots > Create Snapshot.
- Select the volume to snapshot.
- Verify Snapshot:
- Connect to the EC2 instance and create a file:
echo "Test data" > /mnt/data/testfile.txt
- Create a snapshot and note its ID.
- Create Another File:
- Add another file to the instance:
echo "More data" > /mnt/data/testfile2.txt
- Verify that the snapshot does not include the new file (snapshots are point-in-time).
- Create a Volume from Snapshot:
- Use the snapshot to create a new EBS volume.
- Attach the new volume to an instance and mount it to validate the restored data.
Full vs. Incremental Backups
- Full Backup:
- Includes all data in the volume.
- Consumes more storage and time.
- Incremental Backup:
- Stores only changes since the last snapshot.
- Cost-effective and faster.
Summary of Key Points
- Use Multi-Attach Volumes for clustered or shared workloads requiring high availability.
- Select the appropriate volume type based on workload requirements (e.g., gp3 for general-purpose, io2 for high IOPS).
- Understand IOPS and Throughput to optimize performance and costs.
- Snapshots provide a reliable, incremental backup solution stored in S3, enabling disaster recovery and replication.
- Perform regular snapshot verification by creating files, taking snapshots, and testing data recovery.
By mastering these topics, you can effectively manage AWS EBS storage, ensure data durability, and optimize performance for diverse workloads.
Here’s a concise blog-style guide based on your requirements:
Automating EBS Volume Snapshot Management with Recycle Bin and Encryption
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) offers powerful features like snapshots, cross-region copy, encryption, and lifecycle policies. This blog will walk you through practical steps to automate snapshots, activate and use the recycle bin, move snapshots across regions, enable encryption, and restore snapshots to S3.
1. Automating EBS Volume Snapshots
Snapshots are incremental backups of your EBS volumes. Automating them ensures regular backups and operational continuity. Here's how:
- Set up an Automation:
- Use AWS Backup or an Amazon EventBridge rule to schedule snapshots.
- Define a lifecycle policy in Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM) to automatically create and delete snapshots after a specified time.
- Choose Retention Period: Specify the number of days to retain snapshots. Older snapshots will be deleted automatically, minimizing storage costs.
2. What is a Recycle Bin?
The Recycle Bin is a feature that allows you to recover accidentally deleted EBS snapshots and volumes within a specified retention period.
Key Features:
- Works for both snapshots and volumes.
- Configurable retention period based on your needs.
- Ensures recovery options without additional effort.
Steps to Enable the Recycle Bin:
- Go to Recycle Bin in the AWS Management Console.
- Create a new retention rule:
- Specify resource types (EBS volumes or snapshots).
- Define the retention period.
- Save the rule.
3. Using the Recycle Bin Practically
- Create a Snapshot: Navigate to the EBS section, select a volume, and create a snapshot.
- Delete the Snapshot: Go to the snapshot list and delete it.
- Access Recycle Bin: Deleted snapshots will appear in the Recycle Bin during the retention period.
- Recover Snapshots:
- Open the Recycle Bin.
- Select the snapshot.
- Choose "Restore Snapshot."
4. Moving Snapshots Across Regions
Snapshots can be copied to another region for disaster recovery or backup purposes.
Steps:
- Go to the snapshot list in the AWS Console.
- Select the snapshot to copy.
- Click Actions > Copy.
- Choose the destination region and configure settings (e.g., encryption).
- Confirm and initiate the copy.
5. Encryption for EBS Volumes and Snapshots
Encryption enhances data security by encrypting data at rest, in transit, and backups.
Why Encryption Matters:
- Protects sensitive data.
- Complies with regulatory requirements.
- Prevents unauthorized access.
Steps to Encrypt a Volume:
- Create a new EBS volume with encryption enabled (use AWS-managed or custom KMS keys).
- Migrate data to the encrypted volume using the
ebs-encryption-by-defaultsetting for automation.
Impact on Snapshots:
- Snapshots of an encrypted volume are automatically encrypted.
- Encrypted snapshots can only restore to encrypted volumes.
Performance Note: EBS encryption does not impact performance, ensuring seamless operations.
6. Snapshot Restore to S3
You can archive snapshots to Amazon S3 for cost-effective storage.
Steps:
- Open the snapshot page in the AWS Console.
- Select a snapshot and click Actions > Archive to S3.
- Define the archive settings and confirm.
- To restore:
- Access archived snapshots in the "Archive" section.
- Choose "Restore Snapshot" to bring it back to the EBS system.
Conclusion
Automating snapshots, activating the recycle bin, using encryption, and restoring snapshots to S3 are essential steps for efficient EBS volume management. These practices ensure data security, simplify disaster recovery, and optimize costs without compromising performance.
Next Steps:
- Explore AWS Backup for automation.
- Enable encryption by default for enhanced security.
- Leverage cross-region replication for a robust DR strategy.